12dB Crossover
Calculation of a 2nd order loudspeaker crossover with 12dB attenuation per octave
Crossover Calculator
12dB Crossover (2nd Order)
Crossover with two components per way: One inductor and one capacitor for woofer and tweeter. Attenuation: 12dB per octave (Butterworth characteristic).
Circuit Diagram
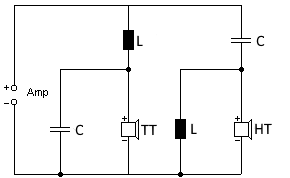
Circuit diagram of a 12dB crossover (2nd order)
The calculated values are automatically inserted into the circuit diagram. Both ways use identical component values.
|
|
|
|
Calculation Formulas
Inductor (Butterworth 2nd Order)
Capacitor (Butterworth 2nd Order)
Variable Legend
| \(L\) | Inductor (Henry) |
| \(C\) | Capacitor (Farad) |
| \(Z\) | Impedance (Ohm) |
| \(f_C\) | Crossover frequency (Hz) |
| \(\sqrt{2}\) | Butterworth factor ≈ 1.414 |
Phase Behavior
With 12dB crossovers, both speakers move in phase. No polarity reversal required!
Characteristics of 12dB Crossover (2nd Order)
Operation
A 2nd order crossover requires 2 components in each branch and provides a slope steepness of 12dB per octave. The values of the capacitors and inductors in the high-pass and low-pass are identical. This crossover is based on the Butterworth characteristic with a Q-factor of 0.707.
Advantages
- Better separation (12dB/octave)
- Standard for HiFi applications
- No polarity reversal required
- Flat frequency response
Disadvantages
- More components required
- Higher costs
- More complex circuit
- Higher losses
Technical Details
Phase Behavior
Since in the low-pass at the crossover frequency, the current lags the voltage by 180° and in the high-pass the voltage also lags the current by 180°, the speaker membranes move in phase.
Butterworth Characteristic
The 12dB crossover uses the Butterworth characteristic with a Q-factor of 0.707. This provides a maximally flat response in the passband.
Typical Application
12dB crossovers are the standard for high-quality HiFi speakers. They provide a good balance between selectivity and phase behavior.
Calculation Example
Given: 8Ω speaker, crossover frequency 2400Hz
\[L = \frac{\sqrt{2} \cdot 8Ω}{2π \times 2400Hz} ≈ 0.75\text{ mH}\]
\[C = \frac{\sqrt{2}}{4π \times 2400Hz \times 8Ω} ≈ 5.9\text{ µF}\]
Comparison of Crossover Orders
| Order | Attenuation | Components per way | Phase behavior | Application |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1st order | 6dB/octave | 1 (L or C) | Polarity reversal needed | Simple systems |
| 2nd order | 12dB/octave | 2 (L and C) | No polarity reversal | HiFi standard |
| 3rd order | 18dB/octave | 3 (L-C-L or C-L-C) | Polarity reversal needed | Professional |
|
|