Abs Function
Abs calculates the absolute value of real or complex numbers
Function
Abs returns the absolute value of a real or complex number. The absolute value of a real or complex number is its distance to zero. This absolute value is always a positive real number.
The argument can be a single number or a data field. For data fields, the absolute value of each element is calculated and the results returned in a data field of equal size.
Syntax
- Abs (real | complex)
- Abs (list)
- Abs (table)
Example with a real number
Abs (-4.56) = 4.56
Abs (4.56) = 4.56
Example with a list of real numbers
x = Rnd (New (12,30)) -15 = -10 -9 2 3 -3 12 13 -2 1 -14 -11 7
Abs (x) = 10 9 2 3 3 12 13 2 1 14 11 7
Example with a complex number
Abs (2 - 5i) = 5.39
Absolute value of a real number
The absolute value of a real number is obtained by omitting the sign. The absolute value of a real number is the distance from the zero point on the number line.
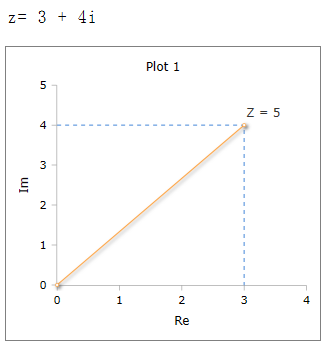
Absolute value of a complex number
The absolute value of a complex number corresponds to the length of the vector.
The absolute value of a complex numbe z = a + bi is ![]()
Visual representation of a complex number and the absolute value z.
For more information about the absolte value see Abs and Tutorial
|
|