Calculate RC High Pass Filter
Calculator and formulas for calculating the parameters of an RC high pass filter
Calculate RC High Pass
RC High Pass Filter
This function calculates the properties of a high pass filter made from a resistor and capacitor. The output voltage, attenuation and phase shift are calculated for the given frequency.
RC High Pass Circuit
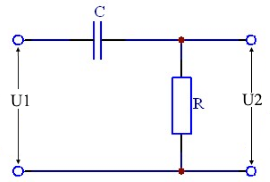
Symbol Explanations
High Pass Characteristics
- Passes high frequencies
- Attenuates low frequencies
- -3dB at cutoff frequency
- +20dB/decade rise
- Phase shift 0° to +90°
Cutoff Frequency
At the cutoff frequency, the attenuation is -3dB.
|
|
RC High Pass - Theory and Formulas
RC High Pass Fundamentals
An RC high pass filter is a first-order filter that passes high frequencies and attenuates low frequencies. The output is taken across the resistor. At low frequencies, the capacitor has high resistance, at high frequencies it has low resistance.
Important Formulas
Voltage Ratio
or simpler with XC:
Reactance
The capacitive reactance decreases with increasing frequency.
Attenuation and Phase
Attenuation in dB
or directly:
Phase Shift
or:
Cutoff Frequency and Characteristic Values
Cutoff Frequency
At fc: Attenuation = -3dB, Phase = 45°
Impedance
Total impedance of the circuit
Time Constant
Characteristic time of the circuit
Frequency Response
Frequency Response Characteristics
- Low frequencies (f ≪ fc): Strong attenuation, Phase → +90°
- Cutoff frequency (f = fc): -3dB attenuation, Phase = +45°
- High frequencies (f ≫ fc): No attenuation, Phase → 0°
- Roll-off rate: +20dB/decade above fc
- Transfer function: H(jω) = jωRC/(1 + jωRC)
Practical Applications
AC Coupling:
High Frequency Filters:
Differentiators:
Design Guidelines
Important Design Aspects
- Cutoff frequency selection: Should be well below the lowest frequency to be transmitted
- Capacitance choice: Larger C → lower fc, but larger components
- Resistance choice: Trade-off between input impedance and signal level
- Loading effects: Following stage should be high impedance
- Tolerances: Component variations affect cutoff frequency
|
|