Points in the Coordinate System
Describe points using coordinates and calculate distances between them
Overview
Points in a plane can be precisely described using coordinates. A coordinate system uses two perpendicular axes (the x-axis and y-axis) to define the position of any point.
The coordinate system divides the plane into four quadrants. Points are described by an ordered pair of numbers (coordinates) that represent their distances from the axes.
Describing Points with Coordinates
Any point in a plane can be described by a pair of numbers, called coordinates.
A point \(A\) is described as \(A(x, y)\), where:
- \(x\) = horizontal distance from the y-axis (x-coordinate)
- \(y\) = vertical distance from the x-axis (y-coordinate)
Sign Conventions
The signs of the coordinates depend on which quadrant the point is in:
- Right of the y-axis: \(x\) is positive
- Left of the y-axis: \(x\) is negative
- Above the x-axis: \(y\) is positive
- Below the x-axis: \(y\) is negative
Visual Example
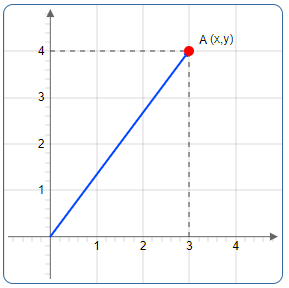
Distance Between Two Points
To find the distance between two points, we use the distance formula, which is derived from the Pythagorean theorem.
The Distance Formula
For two points \(A(x_1, y_1)\) and \(B(x_2, y_2)\), the distance between them is:
This formula comes from the Pythagorean theorem. The distance between two points is the hypotenuse of a right triangle with legs equal to the differences in x and y coordinates.
Worked Example
Calculate Distance Between Two Points
Given: Point \(A(1, 2)\) and Point \(B(4, 5)\)
Find: The distance between points \(A\) and \(B\)
Step 1: Identify the coordinates
\(x_2 = 4, \quad y_2 = 5\)
Step 2: Calculate the differences
\(\Delta y = y_2 - y_1 = 5 - 2 = 3\)
Step 3: Apply the Pythagorean theorem
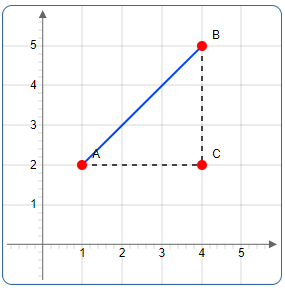
Step 4: Use the distance formula
Step 5: Calculate the distance
Result: The distance between \(A\) and \(B\) is approximately \(4.243\) units (or exactly \(3\sqrt{2}\) units).
Key Concepts
- Coordinates describe position: \(A(x, y)\)
- Distance formula: \(d = \sqrt{(x_2 - x_1)^2 + (y_2 - y_1)^2}\)
- Distance is always positive and symmetric: \(AB = BA\)
- The distance formula is based on the Pythagorean theorem
- Sign of coordinates indicates position relative to axes
- Distance is measured in the same units as the coordinate axes
Learn More
For more detailed examples and exercises on distance calculations between points:
Distance Between Two Points Tutorial →
|
|