Distance Between Two Points
Calculate the distance between any two points using the distance formula
Overview
The distance between two points is the length of the straight line segment connecting them. This can be calculated using the distance formula, which is derived from the Pythagorean theorem.
Distance is always positive and independent of the order of the points: the distance from A to B equals the distance from B to A.
The Distance Formula
To find the distance between two points on a coordinate plane, we use the distance formula, derived from the Pythagorean theorem.
For two points \(A(x_1, y_1)\) and \(B(x_2, y_2)\):
- \(d\) = distance between the two points
- \(x_1, y_1\) = coordinates of the first point
- \(x_2, y_2\) = coordinates of the second point
Worked Example
Calculate Distance Between Two Points
Given: Points \(A(0, -2)\) and \(B(8, 4)\)
Find: The distance between points \(A\) and \(B\)
Step 1: Identify the coordinates
\(x_2 = 8, \quad y_2 = 4\)
Step 2: Calculate the differences
\(y_2 - y_1 = 4 - (-2) = 6\)
Step 3: Square the differences
\((y_2 - y_1)^2 = 6^2 = 36\)
Step 4: Add the squares
Step 5: Take the square root
Result: The distance between points \(A(0, -2)\) and \(B(8, 4)\) is \(10\) units.
Pythagorean Theorem Connection
The distance formula is derived from the Pythagorean theorem. When we connect two points, we form a right triangle where the distance is the hypotenuse.
Geometric Interpretation
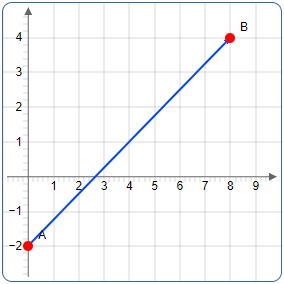
In the right triangle formed by the two points:
- Horizontal side (a): \(a = x_2 - x_1\)
- Vertical side (b): \(b = y_2 - y_1\)
- Hypotenuse (c): \(c = \sqrt{a^2 + b^2}\) = distance
According to the Pythagorean theorem:
Angle to the X-Axis
We can also calculate the angle that the line connecting the two points makes with the x-axis using trigonometric functions.
Angle Formulas
Using inverse sine (arcsin):
Using inverse cosine (arccos):
\(\alpha\) represents the angle between the line segment and the positive x-axis, measured counterclockwise.
Key Points
- Distance formula: \(d = \sqrt{(x_2 - x_1)^2 + (y_2 - y_1)^2}\)
- Distance is derived from the Pythagorean theorem
- Distance is always positive and symmetric: \(AB = BA\)
- The order of the points does not matter
- Distance works with negative coordinates too
- Angle to x-axis can be found using inverse trigonometric functions
Online Calculator
Use the interactive calculator to quickly compute distances and angles between any two points:
Distance Calculator →
|
|