Calculate RL Low-pass Filter
Calculator and formulas for calculating the parameters of an RL low-pass filter
RL Low-pass Filter Calculator
RL Low-pass Filter
This function calculates the properties of a low-pass filter made from a resistor and an inductor. It calculates the output voltage, attenuation, and phase shift at the given frequency.
Circuit Diagram & Parameters
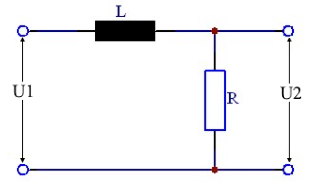
Parameters
|
|
|
|
Example Calculations
Practical Calculation Examples
Example 1: Audio Low-pass Filter
Given: R = 8Ω, L = 1mH, f = 3kHz, U₁ = 10V
Example 2: Cutoff Frequency Calculation
Given: R = 100Ω, L = 10mH
Example 3: Phase Shift
Given: R = 50Ω, L = 5mH, f = 1kHz
Low-pass Filter Characteristics
Frequency Response:
Phase Response:
Formulas for RL Low-pass Filter
Calculate Voltage Ratio
The output voltage U2 of an RL low-pass filter is calculated using the following formula.
Output Voltage
or simpler, when XL is known:
Reactance
The inductive reactance increases proportionally with frequency.
Attenuation in Decibels
The attenuation is 3dB at the cutoff frequency. It can be calculated for different frequencies using the formulas below.
Attenuation (simple)
When input and output voltages are known.
Attenuation (complex)
Direct calculation from R, L and ω.
Phase Shift
In an RL low-pass filter, the output voltage lags the input voltage by 0° to -90° depending on frequency. At the cutoff frequency, the phase shift is -45°.
Phase angle (simple)
Phase angle (complex)
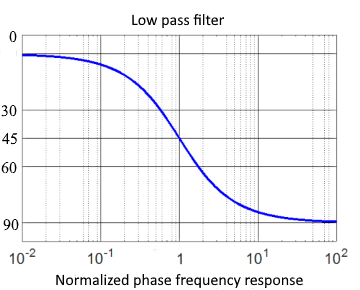
Cutoff Frequency
At cutoff frequency fc, the value of the amplitude-frequency response equals 0.707. This corresponds to –3dB.
Cutoff Frequency Formulas
Practical Applications
Audio Technology
- Subwoofer filters
- Crossover networks
- Noise filters
- Anti-aliasing
Signal Processing
- Smoothing filters
- Integrator
- Interference suppression
- EMC filters
Power Electronics
- Motor chokes
- Mains filters
- Rectifier circuits
- Switch-mode power supplies
|
|