Vector Subtraction
Calculator and formula for subtracting vectors (component-wise difference)
Vector Subtraction Calculator
Vector Subtraction
Calculates the difference v₁ - v₂ of two vectors through component-wise subtraction: [x₁-x₂, y₁-y₂, z₁-z₂]
Requirements for Subtraction
Vectors can only be subtracted if they have the same dimension and the same orientation (column or row vectors).
Subtraction Info
Subtraction Properties
Component-wise: Corresponding elements are subtracted
Not commutative: v₁ - v₂ ≠ v₂ - v₁
Dimension: Same number of components required
Graphic Representation
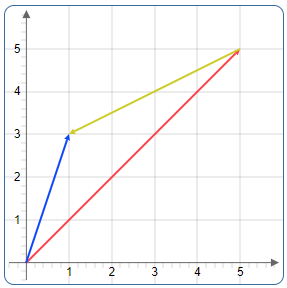
Examples
Formulas for Vector Subtraction
General Formula
Component-wise subtraction
2D Subtraction
Two-dimensional vectors
3D Subtraction
Three-dimensional vectors
Geometric Interpretation
Subtraction as addition of opposite vector
Calculation Examples for Vector Subtraction
Example 1: 2D Subtraction
Result: [2, 1]
Example 2: 3D Subtraction
Result: [9, 18, 27]
Geometric Interpretation
Subtraction creates the vector from the subtrahend to the minuend
Rules and Restrictions
✓ Allowed
• Same dimension
• Same orientation
• [a,b] - [c,d]
✗ Not Allowed
• Different dimensions
• [a,b] - [c,d,e]
• Row vs column vector
⚠ Notice
• Not commutative
• Order matters
• a - b ≠ b - a
Applications of Vector Subtraction
Vector subtraction is fundamental for movement, differences, and direction calculations:
Navigation & Movement
- Direction vector between two points
- Calculate velocity differences
- Relative movement and position change
- GPS navigation and pathfinding
Computer Graphics
- Object movement and transformation
- Collision detection and avoidance
- Camera and view transformations
- Animations and motion interpolation
Physics & Mechanics
- Force and momentum differences
- Calculate relative velocities
- Center of mass and center point
- Field strengths and potentials
Data Analysis
- Differences between datasets
- Trend analysis and change vectors
- Feature differences in ML
- Statistical deviation analysis
Vector Subtraction: Differences in Vector Space
Vector subtraction is a fundamental operation of linear algebra that assigns a difference to two vectors. This component-wise subtraction follows the same rules as scalar arithmetic, but elegantly extends them to higher dimensions. Geometrically interpreted, the subtraction v₁ - v₂ creates the vector pointing from the end of the second vector to the end of the first. This operation is central for movement calculations, direction determination, and the analysis of vector differences in physics and engineering.
Summary
Vector subtraction combines algebraic simplicity with geometric significance. The intuitive rule - subtract corresponding components - opens up fundamental spatial relationships between points and directions. From navigation through computer graphics to physics, vector subtraction enables precise calculations of relative positions, movements, and changes. It demonstrates how elementary mathematical operations quantify and make computationally accessible complex spatial and temporal relationships.
|
|