Elliptic Cone Calculator
Calculator and formulas for calculating an elliptic cone
Elliptic Cone Calculator
The Elliptic Cone
The elliptic cone is a rotational solid with an elliptical base and an apex.
Elliptic Cone Properties
The elliptical cone: Cone with an elliptical base instead of circular
Elliptic Cone Structure
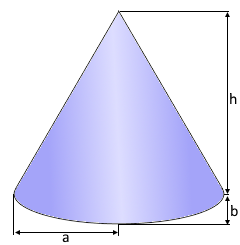
The elliptic cone with oval base.
Two different radii define the ellipse.
|
|
What is an elliptic cone?
The elliptic cone is a fascinating three-dimensional solid:
- Definition: Cone with an elliptical base instead of circular
- Base: Ellipse defined by two different radii (a and b)
- Apex: Single point above the elliptical center
- Lateral surface: Complex curved surface
- Cross-sections: Ellipses parallel to base
- Applications: Engineering and architectural uses
Geometric Properties of the Elliptic Cone
The elliptic cone demonstrates complex geometric relationships:
Basic Parameters
- Short radius (a): Semi-minor axis of ellipse
- Long radius (b): Semi-major axis of ellipse
- Height (h): Distance from apex to base
- Eccentricity: e = √(1 - (a²/b²))
Special Properties
- Non-circular: Base is an ellipse, not a circle
- Complex surface: Lateral area requires integration
- Approximation: Simplified formulas for practical use
- Asymmetric: Different properties in different directions
Mathematical Relationships
The elliptic cone follows complex mathematical laws:
Volume Formula
One third of elliptical base area times height. Simple extension of circular cone.
Surface Formula
Lateral surface requires elliptic integrals. Approximation formulas used in practice.
Applications of the Elliptic Cone
Elliptic cones find applications in specialized fields:
Engineering & Manufacturing
- Specialized nozzles and funnels
- Pressure vessel heads
- Aerodynamic components
- Flow control devices
Architecture & Design
- Elliptical roof structures
- Decorative architectural elements
- Modern sculptural forms
- Specialized structural components
Science & Research
- Optical lens systems
- Acoustic focusing devices
- Particle physics detectors
- Mathematical modeling
Education & Mathematics
- Advanced geometry studies
- Calculus applications
- Engineering mathematics
- 3D modeling exercises
Formulas for Calculating Elliptic Cones
Volume (V)
One third of base area times height
Base Area (A)
Area of the elliptical base
Lateral Area (M) - Exact Formula
Exact lateral surface area using elliptic integral
Lateral Area (M) - Approximation
Simplified approximation formula for practical calculations
Total Surface (S)
Base area plus lateral surface area
Eccentricity (e)
Eccentricity of the elliptical base
Calculation Example for an Elliptic Cone
Given
Find: All properties of the elliptic cone
1. Base Area Calculation
For a = 2, b = 3:
\[A = a \cdot b \cdot \pi\] \[A = 2 \cdot 3 \cdot \pi = 6\pi\] \[A ≈ 18.85\]The base area is approximately 18.85 square units
2. Volume Calculation
For A = 6π, h = 4:
\[V = \frac{h \cdot A}{3}\] \[V = \frac{4 \cdot 6\pi}{3} = 8\pi\] \[V ≈ 25.13\]The volume is approximately 25.13 cubic units
3. Lateral Area Calculation
Using approximation formula:
\[M ≈ \frac{\pi}{2}(a\sqrt{b^2+h^2} + b\sqrt{a^2+h^2})\] \[M ≈ \frac{\pi}{2}(2\sqrt{25} + 3\sqrt{20})\] \[M ≈ \frac{\pi}{2}(10 + 13.42) ≈ 36.78\]The lateral area is approximately 36.78 square units
4. Total Surface Calculation
Base area + lateral area:
\[S = A + M\] \[S ≈ 18.85 + 36.78\] \[S ≈ 55.63\]The total surface is approximately 55.63 square units
5. The Perfect Elliptic Cone
The elliptic cone with perfect oval symmetry
Note on Approximation
The lateral surface calculation uses an approximation formula. For a = 2, b = 3, h = 4, the approximation gives 36.78, while the exact value using elliptic integrals is approximately 36.9. The approximation is slightly below the exact value but provides good practical accuracy.
The Elliptic Cone: Complex Geometry in Perfect Form
The elliptic cone represents a fascinating extension of classical cone geometry, where the circular base is replaced by an ellipse. This seemingly simple modification introduces remarkable mathematical complexity, requiring advanced calculus and elliptic integrals for exact solutions. The elliptic cone bridges pure geometry with practical engineering applications, demonstrating how mathematical sophistication often underlies seemingly simple three-dimensional forms. Its study reveals the deep connections between elementary geometry, advanced calculus, and real-world applications in fields ranging from aerospace engineering to architectural design.
The Geometry of Elliptical Extension
The elliptic cone demonstrates the complexity that emerges from geometric generalization:
- Elliptical base: Defined by two different radii (semi-major and semi-minor axes)
- Non-uniform scaling: Different properties in different directions
- Complex lateral surface: Requires elliptic integrals for exact calculation
- Practical approximations: Simplified formulas for engineering applications
- Eccentricity effects: Shape varies from circular (e=0) to highly elliptical
- Cross-sectional similarity: All parallel cuts produce similar ellipses
- Engineering versatility: Optimal for specialized flow and structural applications
Mathematical Sophistication
Volume Simplicity
Despite the complex base, the volume formula remains elegantly simple: one third of the elliptical base area times height.
Surface Complexity
The lateral surface area requires elliptic integrals for exact calculation, showcasing the mathematical depth beneath geometric forms.
Practical Approximations
Engineering applications use simplified approximation formulas that provide excellent accuracy while avoiding complex integrals.
Specialized Applications
The elliptic cone's unique properties make it ideal for applications requiring directional flow characteristics or specialized structural properties.
Summary
The elliptic cone stands as a testament to the mathematical richness that emerges when classical geometric forms are generalized. Its elliptical base introduces complexities that require advanced mathematical tools, yet its practical applications demonstrate the value of this sophistication. From the simple volume formula to the complex elliptic integrals needed for exact surface calculations, the elliptic cone bridges elementary and advanced mathematics. In engineering and architecture, it provides solutions for specialized applications where circular symmetry is insufficient. The elliptic cone reminds us that mathematical complexity often underlies practical utility, and that the pursuit of geometric generalization leads to both theoretical insights and real-world innovations.