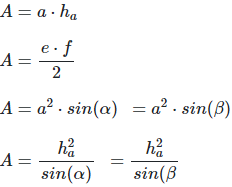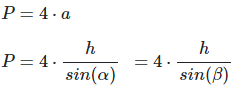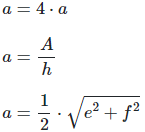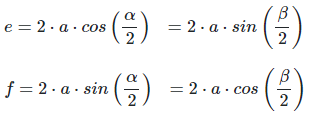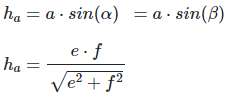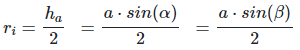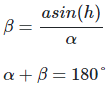Rhombus
Rhombus formulas and properties
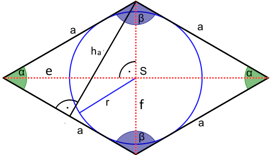
A rhombus is a flat quadrangule with four sides of equal length. Opposite sides are parallel and opposite angles are equal. Alternatively, the rhombus can also be defined as a parallelogram whose diagonals intersect each other at right angles.
Properties
- Opposite sides are parallel.
- Opposite interior angles are the same size, adjacent interior angles are supplementary, their sum is 180°.
- The interior angles are bisected by a diagonal.
- The two diagonals are perpendicular to each other and bisect each other.
- It has an incircle and is therefore a tangent quadrilateral. The center of the circle is the intersection of the diagonals.
Formulas
Area
Perimeter
Side length
Length of the diagonals
Height
Inner circle radius
Interior angle
Rhombus online calculator →
|
|