Parallelogram
Properties and formulas for calculation of a parallelogram
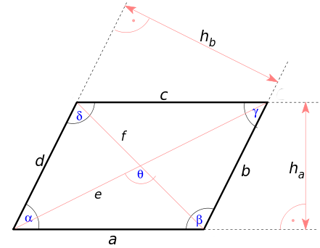
A parallelogram or rhomboid is a convex flat quadrilateral in which the opposite sides are parallel.
Properties
- Two opposite sides are parallel and of equal length.
- Opposite angles are the same size.
- Any two adjacent angles add up to 180°.
- The diagonals bisect each other.
Formeln
Area
\(\displaystyle A=a·h_a \ \ =b·h_b \)
\(\displaystyle A=a·b·sin(α)\ \ =a·b·sin(β) \)
Perimeter
\(\displaystyle P = 2·a+2·b \ \ = 2 ·(a + b)\)
\(\displaystyle P = 2 · \frac{h_a}{sin(α)} + (2 · b)\)
Height
\(\displaystyle h_a = sin(α) · a \ \ = sin(β) · a\)
\(\displaystyle h_a = \frac{A}{b}\)
\(\displaystyle h_b = sin(α) · b \ \ = sin(β) · b\)
\(\displaystyle h_b = \frac{A}{a}\)
Diagonal
\(\displaystyle e = \sqrt{a^2 + b^2 - 2 · a · b · cos(β)}\)
\(\displaystyle e = \sqrt{a^2 + b^2 + 2 · a · b · cos(α)}\)
\(\displaystyle f = \sqrt{a^2 + b^2 - 2 · a · b · cos(α)}\)
\(\displaystyle f = \sqrt{a^2 + b^2 + 2 · a · b · cos(β)}\)
Interior angle
\(\displaystyle α=γ, \ \ β=δ, \ \ α+β=180°\)
\(\displaystyle α=asin\left(\frac{A}{a·b}\right)\)
Parallelogram equation
\(\displaystyle e^2+f^2 = 2 ·(a^2 + b^2)\)
Parallelogram online calculator →
|
|