RMS value of a square wave voltage
Calculator and formulas for calculating the RMS value of a square wave voltage
Square Wave Calculator
Square wave (50% duty cycle)
It is assumed that the pulse duration (ti) and the pause (tp) have the same length (50% duty cycle).
|
|
Square wave & parameters
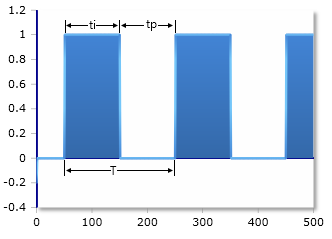
Parameters
Formulas (50% duty cycle)
|
|
Example calculations
Practical calculation examples
Example 1: Standard square wave
Given: Us = 10V (50% duty cycle)
Example 2: Digital logic voltage
Given: Us = 5V (TTL level, 50% duty cycle)
Example 3: Symmetrical AC square wave
Given: Us = 10V (±5V square AC voltage)
Comparison of square wave types
Square pulse voltage (0V to Us):
Square AC voltage (-Us to +Us):
Formulas for square wave
What is a square wave voltage?
The RMS value of a square pulse voltage depends on how the voltage changes over time. A square pulse voltage usually has a fixed peak value Us and alternates between two voltage values over time, for example Us and 0 V or Us and -Us.
The calculator above computes the variant with Us and 0 V. The time at Us and 0 V (ti and tp) is 50% each. For a calculator with variable pulse length, see here.
Definition of RMS value
The RMS value is defined as the DC value with the same thermal effect as the considered AC value.
Square pulse voltage (0V to Us)

The RMS value for square waves with equal pulse duration (ti) and pause (tp) is:
RMS value
About 70.7% of the peak voltage.
Mean value
Half the peak voltage.
Square AC voltage (-Us to +Us)
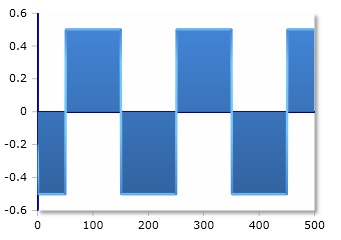
For a symmetrical square AC voltage, the RMS value is equal to the peak value:
Symmetrical AC voltage
Since the voltage in both cases has the same magnitude (but different sign), the RMS value remains equal to the amplitude of the square wave.
The mean value for a symmetrical square AC voltage is always 0 volts.
Mathematical derivation
Calculation of RMS value
For a square wave with 50% duty cycle over a period T:
Practical applications
Digital technology
- TTL/CMOS logic levels
- Clock signals (50% duty cycle)
- Data transmission
- Microcontroller outputs
Power electronics
- Inverters
- DC-AC converters
- H-bridges
- Motor control
Signal processing
- Modulation methods
- Reference signals
- Test signals
- Calibration
Spectral properties
Harmonics in square waves
Square waves contain all odd harmonics:
Design notes
Practical considerations
- Power dissipation: P = Ueff²/R - reduced at 50% duty cycle
- EMC: Square waves generate many harmonics
- Filtering: Low-pass filters required for harmonic suppression
- Switching times: Real square waves have finite edge times
- Coupling: Transformers suitable for AC transmission
- Measurement technology: True-RMS meters for correct RMS measurement
|
|