RMS and Peak Value of a Sine Wave
Calculator and formulas for calculating the RMS or peak value of a sine wave
Sine RMS-Peak Voltage
Sine Wave
The voltage can be entered as RMS or peak value. The input of the peak value is preset.
|
|
Sine Wave & Parameters
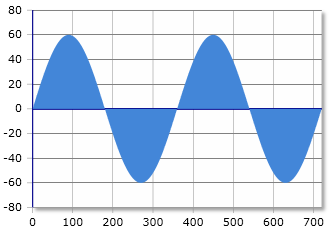
Parameters
Basic formulas
|
|
Example calculations
Practical calculation examples
Example 1: Household voltage
Given: Ueff = 230V (mains voltage)
Example 2: Signal generator
Given: Us = 10V (peak voltage)
Example 3: Audio signal
Given: Ueff = 1.41V (audio level)
Ratios for sine wave
RMS ratio:
Peak value ratio:
Formulas for Sine Wave
What is a sine wave?
The RMS value is defined as the DC value with the same thermal effect as the considered AC value. For a sinusoidal AC, it is the characteristic value of 1/√2 of the peak value.
Definition of RMS value
In a sine wave, the voltage oscillates harmonically between -Us and +Us. The mean value of the pure sine wave is always 0 volts. If the voltage is superimposed by a DC voltage, the mean value corresponds to the superimposed DC voltage.
Calculate RMS value
The RMS value is about 70.7% of the peak voltage.
Calculate peak value
The peak value is about 141.4% of the RMS value.
Mathematical derivation
Calculation of the RMS value
For a sine wave u(t) = Us · sin(ωt) over a period T:
Practical applications
Power engineering
- Mains voltage (230V RMS)
- Transformers
- Generators
- Motor control
Signal technology
- Signal generators
- Oscillators
- Modulation carriers
- Reference signals
Audio/RF technology
- Audio amplifiers
- Radio transmission
- Antenna signals
- Measuring instruments
Measurement aspects
Important measurement notes
Moving-coil meters can only measure the half-wave mean value, but due to the corresponding calibration of the scale, they display the RMS value. If a non-sinusoidal value is measured, incorrect readings are obtained.
Measure correct RMS values
even for distorted signals
Only correctly calibrated
for pure sine signals
Show peak values
Conversion required
Spectral properties
Pure sine wave
An ideal sine voltage contains only a single frequency component:
Comparison with other waveforms
Crest factors of different signals
Peak-to-RMS ratio:
Practical significance:
Design notes
Important considerations
- Insulation: Dimension voltage resistance according to peak value
- Heating: Calculate power dissipation according to RMS value
- Measurement accuracy: Use true-RMS meters for distorted signals
- Overdrive: Consider crest factor for amplifiers
- Power quality: Harmonics reduce ideal sine waveform
- Safety: Design touch protection according to peak voltage
|
|