Parameters of Alternating Voltage
Calculator and formulas for calculating RMS and average values for AC voltage
Calculate Sine Parameters
AC Voltage Parameters
This function calculates the sine parameters for RMS voltage, peak voltage, peak-to-peak voltage, and rectified voltage from the specified voltage. RMS voltage is preset for input.
|
|
Sine Parameters
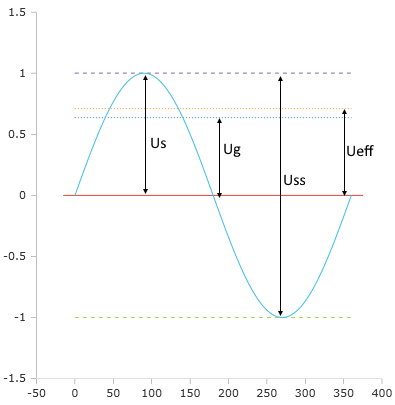
Sine voltage parameters
Parameters
Basic formulas
|
|
Conversion factors
Factors between the parameters
From RMS value to:
× √2 ≈ × 1.414× 2√2 ≈ × 2.828÷ 1.11 ≈ × 0.9To RMS value from:
÷ √2 ≈ × 0.707÷ 2√2 ≈ × 0.354× 1.11Example calculations
Practical calculation examples
Example 1: Mains voltage (230V RMS)
Given: Urms = 230V (European mains voltage)
Example 2: Low voltage (12V RMS)
Given: Urms = 12V (low voltage)
Example 3: Signal voltage (1V peak)
Given: Us = 1V (peak voltage)
Parameter ratios
Crest factor:
Form factor:
Peak-to-peak:
Rectified value:
Parameters and Formulas
AC Voltage Generation
When generating voltage in a rotating generator, a time-varying sinusoidal and periodically repeating AC voltage is produced.
Nominal value and RMS value
The RMS value of an AC voltage Urms is the value that produces the same heat in a resistor as an equal DC voltage. When "230 V" is mentioned for household AC voltage, it refers to the RMS value.
If the peak value is known, the RMS value can be calculated using the following formula:
RMS value formula
The RMS value corresponds to the Root Mean Square (RMS).
Maximum value, peak value, amplitude
The peak value is the highest voltage reached in a sinusoidal waveform. If the RMS value is given, the peak value can be calculated as follows:
Peak value formula
The peak value is √2 times greater than the RMS value.
Peak-to-peak voltage
The peak-to-peak voltage Uss is the difference between the positive and negative peak values, i.e., twice the peak value.
Peak-to-peak formula
The peak-to-peak voltage covers the entire voltage range.
Rectified value
The rectified value is the arithmetic mean of the rectified AC voltage. For pure sine voltages, it can be calculated simply by dividing the RMS voltage by 1.111.
Rectified value formula
The rectified value corresponds to the arithmetic mean after full-wave rectification.
Important factors
Form factor
The form factor is the ratio of the RMS value to the rectified value. For sinusoidal AC voltage, it is 1.111 (exactly π/√8).
Crest factor
The crest factor is the ratio of the peak value to the RMS value. For a sine wave, the crest factor is 1.414 (exactly √2).
Practical applications
Electrical engineering
- Mains voltage specifications
- Transformer design
- Insulation coordination
- Power calculations
Measurement technology
- Oscilloscope measurements
- Multimeter displays
- Signal analysis
- Calibration
Electronics
- Amplifier drive
- ADC range setting
- Voltage regulator design
- EMC considerations
Design notes
Practical considerations
- Voltage withstand: Components must be rated for peak voltage
- Power calculation: Use RMS values for thermal calculations
- Measuring instruments: Distinguish between true-RMS and average-detecting multimeters
- Safety: Consider peak voltages for insulation distances
- Transformers: Core design is based on RMS values
- Capacitors: Voltage rating must be at least for peak voltage
|
|