RMS value of a triangular pulse
Calculator and formulas for calculating the RMS and mean value of a triangular pulse
Triangular Pulse Calculator
Triangular Pulse
This function calculates the RMS and mean value of a triangular pulse. Enter the value of the peak voltage for the calculation.
|
|
Triangular Pulse & Parameters
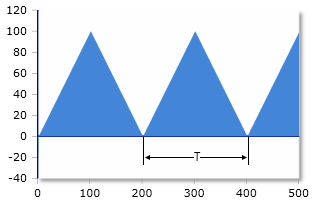
Parameters
Basic formulas
|
|
Example calculations
Practical calculation examples
Example 1: Standard triangular pulse
Given: Us = 10V
Example 2: Audio application
Given: Us = 3V (typical audio level)
Example 3: High voltage
Given: Us = 100V
Ratios for triangular pulse
RMS ratio:
Mean value ratio:
Formula for triangular pulse
What is a triangular pulse?
The RMS value of a triangular pulse (usually referred to as a triangular voltage with periodic pulses) can be calculated in a similar way as the RMS value of a classic triangular wave. It is important that the triangular voltage has a symmetrical shape, where the voltage alternates between positive and negative peak values.
Definition of RMS value
The RMS value is defined as the DC value with the same thermal effect as the considered AC value. For triangular pulses, it is calculated using the following formula:
RMS value
The RMS value is about 57.7% of the peak voltage.
Mean value
The mean value is 50% of the peak voltage.
Mathematical derivation
Calculation
For a symmetrical triangular pulse with period T and peak voltage Us:
Practical applications
Signal generation
- Function generators
- Modulation methods
- Test signals
- Sweep generators
Measurement technology
- Oscilloscopes
- Spectrum analyzers
- RMS measurement
- Calibration
Power electronics
- PWM signals
- Triangle comparators
- Switching regulators
- Motor control
Comparison with other signal forms
RMS factors
Ueff = Us/√2 ≈ 0,707
Ueff = Us/√3 ≈ 0,577
Ueff = Us = 1,0
Ueff = Us/√3 ≈ 0,577
|
|