Half Square Kite Calculator
Calculator and formulas for calculating the properties of a half square kite
Half Square Kite Calculator
The Half Square Kite
A half square kite is a special kite with a right angle at one of the non-symmetrical corners.
Half Square Kite Structure
A half square kite has a right angle.
The diagonals are perpendicular.
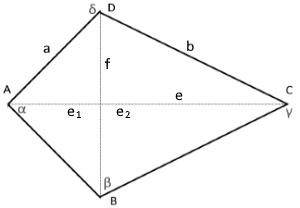
● Side a ● Side b ● Right angle (90°)
|
|
What is a Half Square Kite?
A half square kite is a special type of kite quadrilateral with unique geometric properties:
- Definition: Kite with a right angle (90°) at one non-symmetrical corner
- Perpendicular diagonals: Diagonals e and f meet at right angles
- Symmetry axis: Diagonal e (from A to C) is the axis of symmetry
- Isosceles triangles: Diagonal f divides the kite into two isosceles triangles
- Equal opposite angles: Angles at corners B and D are equal
- Adjacent equal sides: Two pairs of adjacent sides are equal
Geometric Properties
The half square kite possesses special geometric properties:
Side and Angle Properties
- Right angle: One corner has exactly 90°
- Adjacent equal sides: AB = AD and CB = CD
- Four vertices: Points A, B, C, D form the kite
- Angle α: Right angle (90°) at point A
Diagonal Properties
- Perpendicular: Diagonals e and f intersect at 90°
- Symmetry diagonal e: Axis of symmetry of the kite
- Diagonal f: f = √2 · a (special relationship)
- Sections: e₁ and e₂ are segments of diagonal e
Mathematical Relationships
The half square kite follows precise mathematical formulas:
Area Calculation
The area combines the square of side a with the product of diagonal segments.
Perimeter Calculation
The perimeter is twice the sum of the two different side lengths.
Formulas for the Half Square Kite
Side length a
Calculate side a from area and other parameters
Side length b
Calculate side b from area and angle β
Area A
Area formula using side and diagonal segments
Perimeter P
Sum of all four sides
Diagonal e
Using law of cosines
Diagonal f
Special relationship for half square kite
Angle γ
Angle at symmetrical corners
Angle β
Angle at corners B and D
Section e₁
First segment of diagonal e
Right Angle Property
Defining characteristic
Calculation Example
Given
Find: All properties of the half square kite
1. Calculate Diagonal f
Diagonal f using the special formula
2. Calculate Perimeter
Total perimeter of the kite
3. Calculate Angle γ
Angle at symmetrical corners
4. Calculate Angle β
Angle at corners B and D
5. Calculate Section e₁
First segment of diagonal e
6. Calculate Diagonal e
Symmetry diagonal using law of cosines
7. Summary of Results
Complete properties of a half square kite with sides a=3 and b=5
Applications of Half Square Kites
Half square kites appear in various practical applications:
Architecture & Design
- Floor tile patterns and mosaics
- Window and door frame designs
- Decorative wall elements
- Geometric artwork and murals
Crafts & Art
- Origami and paper folding
- Quilting patterns
- Stained glass designs
- Geometric sculpture
Mathematics Education
- Teaching geometric properties
- Demonstrating angle relationships
- Exploring symmetry concepts
- Pythagorean theorem applications
Engineering
- Structural bracing systems
- Mechanical linkages
- Roof truss components
- Frame design elements
The Half Square Kite: Special Geometry
The half square kite is a fascinating special case among kite quadrilaterals. Its defining characteristic — a right angle at one of the non-symmetrical corners — creates unique geometric relationships and elegant mathematical properties.
Definition and Fundamental Properties
The half square kite is characterized by several key features:
- Right angle constraint: One corner (typically point A) has exactly 90°
- Kite properties retained: Two pairs of adjacent equal sides (AB = AD, CB = CD)
- Perpendicular diagonals: Diagonals e and f meet at right angles
- Symmetry axis: Diagonal e serves as the axis of symmetry
- Special diagonal relationship: f = √2 · a (unique to this kite type)
The Special Diagonal Formula
One of the most elegant properties of the half square kite:
Why f = √2 · a?
Because of the right angle at corner A, the diagonal f forms the hypotenuse of an isosceles right triangle with legs of length a. The √2 factor comes directly from the Pythagorean theorem: a² + a² = f², so f = a√2.
Geometric Insight
The half square kite can be thought of as half of a square (hence the name) that has been "pulled" along one diagonal. The right angle property preserves the √2 relationship from the original square.
Connection to Squares
If you place two identical half square kites together along their diagonal e, you can form a square with side length a. This construction demonstrates why the shape is called a "half square" kite.
Angular Relationships
The angles satisfy: α = 90°, and the other angles are determined by the constraint that β appears twice and γ appears once, with 2β + γ + 90° = 360°.
Mathematical Elegance
The half square kite demonstrates several beautiful mathematical principles:
Pythagorean Relationships
The right angle creates multiple right triangles within the kite, each governed by the Pythagorean theorem. The diagonal e can be calculated using the law of cosines, showcasing the interplay between trigonometry and geometry.
Symmetry and Calculation
The axis of symmetry along diagonal e simplifies many calculations. Properties on one side of this axis are mirrored on the other, reducing computational complexity.
Area Formula Derivation
The area formula A = (a² + e₂·f)/2 can be derived by decomposing the kite into triangles. The right angle creates a natural partitioning that leads to this elegant expression.
Inscribed Circle
Like all kites, the half square kite is a tangential quadrilateral — it has an inscribed circle (incircle). The inner radius ri can be calculated from the area and semiperimeter: ri = A/s where s = (a+b).
Related Geometric Shapes
The half square kite connects to other important geometric figures:
Square (When a = b)
When the two side lengths become equal (a = b), the half square kite degenerates into an actual square. All angles become 90°, demonstrating the square as a limiting case.
General Kite
The half square kite is a special case of the general kite where one angle happens to be 90°. All general kite properties apply, plus additional constraints from the right angle.
Right Triangle Components
The kite can be decomposed into two right triangles and one isosceles triangle, providing multiple approaches to calculation and proof.
Isosceles Right Triangle
The right angle corner with two equal sides creates an isosceles right triangle (45-45-90 triangle), connecting to this fundamental geometric object.
Summary
The half square kite exemplifies how adding a single constraint (a right angle) to an already special shape (the kite) creates a wealth of elegant mathematical relationships. The √2 factor in the diagonal formula, the connection to squares, and the multiple right triangles within the shape all contribute to its mathematical beauty. From tiling patterns to structural engineering, this geometric figure demonstrates that simple constraints can lead to rich mathematical structures. The half square kite reminds us that geometry is full of special cases that reveal universal mathematical truths.
|
|
|
|