Sin - Calculate Sine
Online calculator for calculating the sine of an angle
Sine Calculator
Instructions
Enter the angle whose sine you want to calculate, select the unit of measure (degrees or radians) and click Calculate.
Sine - Overview
Value Range
The angle is given in degrees (full circle = 360°) or radians (full circle = 2·π). The result always lies in the range from -1 to +1.
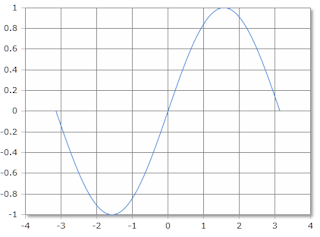
Sine, scale in radians
Definition in Triangle
The sine of an angle α corresponds to the ratio of the opposite side to the hypotenuse in a right triangle.
\(\displaystyle \sin(\alpha) = \frac{\text{Opposite}}{\text{Hypotenuse}} = \frac{a}{c} \)

Important Values
- \( \sin(0°) = 0 \)
- \( \sin(30°) = 0.5 \)
- \( \sin(45°) = \frac{\sqrt{2}}{2} \approx 0.707 \)
- \( \sin(60°) = \frac{\sqrt{3}}{2} \approx 0.866 \)
- \( \sin(90°) = 1 \)
- \( \sin(180°) = 0 \)
|
|
Description of the Sine
Fundamentals
The sine is one of the fundamental trigonometric functions. In a right triangle, the sine of an angle α is the ratio of the opposite side to the hypotenuse.
Definition:
\(\displaystyle \sin(\alpha) = \frac{\text{Opposite}}{\text{Hypotenuse}} \)
\(\displaystyle \sin(\alpha) = \frac{a}{c} \)
Properties
The sine function has several important properties:
- Periodic: sin(α + 360°) = sin(α)
- Odd function: sin(-α) = -sin(α)
- Range: -1 ≤ sin(α) ≤ 1
- Domain: All real numbers
Relationship to Cosine
Sine and cosine are closely related:
\(\displaystyle \sin(\alpha) = \cos(90° - \alpha) \)
\(\displaystyle \sin^2(\alpha) + \cos^2(\alpha) = 1 \)
Detailed Examples
Example 1: Calculate Sine
Given:
A right triangle with:
- Opposite side (to α): \( a = 3 \text{ cm} \)
- Hypotenuse: \( c = 5 \text{ cm} \)
Calculation:
\(\displaystyle \sin(\alpha) = \frac{3}{5} = 0.6 \)
To find the angle: \( \alpha = \arcsin(0.6) \approx 36.87° \)
Example 2: Known Angles
Important sine values:
| \( \sin(0°) \) | = | 0 |
| \( \sin(30°) \) | = | 0.5 |
| \( \sin(45°) \) | = | \( \frac{\sqrt{2}}{2} \approx 0.707 \) |
| \( \sin(60°) \) | = | \( \frac{\sqrt{3}}{2} \approx 0.866 \) |
| \( \sin(90°) \) | = | 1 |
| \( \sin(180°) \) | = | 0 |
Example 3: Practical Application
Task:
A ladder leans against a wall at an angle of 70° to the ground. The ladder is 5 m long. How high up the wall does the ladder reach?
Solution:
\(\displaystyle \text{Height} = 5 \cdot \sin(70°) \approx 5 \cdot 0.94 = 4.7 \text{ m} \)
Conversion
From degrees to radians:
\(\displaystyle \text{Radians} = \frac{\text{Degrees} \cdot \pi}{180°} \)
Mathematical Properties
- Period: 360° or 2π (radians)
- Symmetry: Odd function: sin(-α) = -sin(α)
- Zeros: At 0°, ±180°, ±360°, ...
- Extrema:
- Maximum: 1 at 90°, 450°, ...
- Minimum: -1 at 270°, -90°, ...
- Addition formulas:
- \( \sin(\alpha + \beta) = \sin\alpha\cos\beta + \cos\alpha\sin\beta \)
- \( \sin(\alpha - \beta) = \sin\alpha\cos\beta - \cos\alpha\sin\beta \)
Practical Applications
- Physics: Oscillations and wave mechanics
- Navigation: Course calculations and positioning
- Engineering: Structural analysis and mechanics
- Astronomy: Calculation of celestial positions
- Music: Sound wave analysis
- Signal processing: Fourier analysis
- Computer graphics: Animations and rotations
- Surveying: Height and distance measurements
Important Note
The sine is a periodic function with a period of 360° or 2π. This means that sin(α) = sin(α + 360°). The range always lies between -1 and +1, regardless of the input angle. The sine function is an odd function, i.e., point-symmetric about the origin: sin(-α) = -sin(α). Together with cosine, the sine satisfies the fundamental trigonometric identity: sin²(α) + cos²(α) = 1, known as the Pythagorean identity. The sine function is fundamental in describing periodic phenomena such as waves, oscillations, and circular motion.
|
|