ASec - Arcsecant (Inverse Secant)
Online calculator for calculating the angle to the secant
Arcsecant Calculator
Instructions
Enter the value of the secant (≤-1 or ≥1), select the unit of measure (degrees or radians) and click Calculate.
Arcsecant - Overview
Value Range
The arcsecant is only defined for certain values.
- Domain: x ≤ -1 or x ≥ 1
- Range: [0, π] excluding π/2, or [0°, 180°] excluding 90°
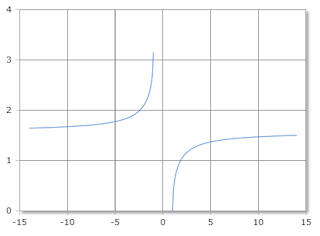
Inverse secant, scale in radians
Definition
The arcsecant (arcsec, asec, or sec⁻¹) is the inverse function of the secant function.
\(\displaystyle y = \text{arcsec}(x) \Leftrightarrow \sec(y) = x \)
with \( |x| \geq 1 \) and \( y \in [0, \pi] \setminus \{\frac{\pi}{2}\} \)
Relationship
Relationship to arccosine:
\(\displaystyle \text{arcsec}(x) = \arccos\left(\frac{1}{x}\right) \)
|
|
Description of the Arcsecant
Fundamentals
The arcsecant (arcsec, asec, or sec⁻¹) is the inverse function of the secant function. It calculates the angle for a given secant value. The secant is the reciprocal of the cosine function.
Mathematical Definition:
\(\displaystyle y = \text{arcsec}(x) \)
means
\(\displaystyle \sec(y) = x \)
Understanding Secant
The secant is a trigonometric function that is the reciprocal of the cosine function. In a right triangle:
\(\displaystyle \sec(\alpha) = \frac{1}{\cos(\alpha)} = \frac{\text{Hypotenuse}}{\text{Adjacent side}} \)
Important: The secant is undefined when cos(α) = 0, which occurs at 90°, 270°, etc. (or π/2, 3π/2, etc. in radians).
Detailed Examples
Example 1: Calculate Secant Value
Given:
An angle α = 60° (or π/3 radians)
Calculating the secant:
\(\displaystyle \sec(60°) = \frac{1}{\cos(60°)} = \frac{1}{0.5} = 2 \)
Example 2: Calculate Angle
Task:
Calculate the angle α for \( \sec(\alpha) = 2 \)
In radians:
\(\displaystyle \alpha = \text{arcsec}(2) = \arccos\left(\frac{1}{2}\right) = \frac{\pi}{3} \approx 1.047 \text{ rad} \)
Conversion to degrees:
\(\displaystyle \alpha = 60° \)
Example 3: Using Triangle
Given:
A right triangle with:
- Hypotenuse: c = 10
- Adjacent side: b = 6
Calculation:
\(\displaystyle \sec(\alpha) = \frac{10}{6} \approx 1.667 \)
\(\displaystyle \alpha = \text{arcsec}(1.667) \approx 53.13° \)
Conversion Formula
From radians to degrees:
\(\displaystyle \text{Degrees} = \frac{\text{Radians} \cdot 180°}{\pi} \)
Properties
- Domain: \( x \leq -1 \) or \( x \geq 1 \)
- Range: \( y \in [0, \pi] \setminus \{\frac{\pi}{2}\} \) (radians) or \( [0°, 180°] \setminus \{90°\} \)
- Discontinuity: Undefined at x = 0 and y = π/2
- Reciprocal: \( \sec(x) = \frac{1}{\cos(x)} \)
- Special values:
- \( \text{arcsec}(1) = 0 \)
- \( \text{arcsec}(2) = \frac{\pi}{3} = 60° \)
- \( \text{arcsec}(-1) = \pi = 180° \)
- \( \text{arcsec}(\sqrt{2}) = \frac{\pi}{4} = 45° \)
Practical Applications
- Physics: Wave analysis and optics
- Engineering: Structural mechanics
- Astronomy: Calculating viewing angles
- Navigation: Distance and position calculations
- Surveying: Angle measurements
- Computer graphics: 3D transformations
- Cryptography: Mathematical algorithms
Relationships to Other Functions
Cosine relationship:
\(\displaystyle \sec(\alpha) = \frac{1}{\cos(\alpha)} \)
\(\displaystyle \cos(\alpha) = \frac{1}{\sec(\alpha)} \)
Arccosine relationship:
\(\displaystyle \text{arcsec}(x) = \arccos\left(\frac{1}{x}\right) \)
for \( |x| \geq 1 \)
Pythagorean Identity
\(\displaystyle 1 + \tan^2(\alpha) = \sec^2(\alpha) \)
This identity relates the secant to the tangent
Important Note
Domain restriction: The arcsecant is only defined for values where \( |x| \geq 1 \). For values between -1 and 1, the function is undefined because the cosine function (whose reciprocal is the secant) only produces values in the range [-1, 1].
Programming: Many programming languages do not have a
built-in arcsecant function. It can be calculated using:
asec(x) = acos(1/x).
|
|