Inverse Hyperbolic Cotangent
Online calculator for calculating the angle to the inverse hyperbolic cotangent
ACoth Calculator
Domain Restriction
The ACoth(x) or inverse hyperbolic cotangent shows inverse function behavior with domain |x| > 1.
ACoth Function Curve
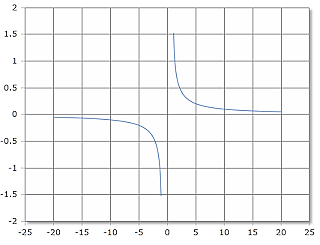
The ACoth function has two separate branches with a gap at [-1, 1].
Domain: (-∞, -1) ∪ (1, ∞), Range: ℝ
|
|
Inverse Function Behavior of ACoth
The inverse hyperbolic cotangent function exhibits characteristic inverse properties:
- Domain: (-∞, -1) ∪ (1, ∞) (|x| > 1)
- Range: ℝ (all real numbers)
- Discontinuity: Gap at [-1, 1]
- Inverse: Coth(ACoth(x)) = x for |x| > 1
- Branches: Two separate monotonic branches
- Asymptotes: Vertical at x = ±1
Logarithmic Representation of ACoth Function
The inverse hyperbolic cotangent function is expressed through logarithmic functions:
Basic Formula
Natural logarithm expression for |x| > 1
Inverse Relation
For |x| > 1
Formulas for the ACoth Function
Definition
Natural logarithm expression for |x| > 1
Inverse Relation
Fundamental inverse function properties
Derivative
First derivative for |x| > 1
Domain Restriction
Returns NaN for -1 ≤ x ≤ 1
Branch Behavior
Two separate monotonic branches
Special Values
Important Values
Invalid Range
Function undefined in interval [-1, 1]
Asymptotes
Function approaches ±∞ at x = ±1
Properties
- Inverse function
- Two separate branches
- Odd function symmetry
- Logarithmic singularities
Branch Limits
Divergent behavior at boundaries
Applications
Statistical mechanics, signal processing, inverse hyperbolic problems, mathematical physics.
Detailed Description of the ACoth Function
Definition and Input
The inverse hyperbolic cotangent function ACoth(x) is the inverse function of the hyperbolic cotangent. It exhibits characteristic two-branch behavior with a restricted domain.
Input
The argument must be less than -1 or greater than 1. Values in the interval [-1, 1] return NaN (not a valid number).
Result
The result is given in degrees (full circle = 360°) or radians (full circle = 2π). The unit of measurement used is set using the Degrees or Radians menu.
Using the Calculator
Enter a value with absolute value greater than 1. The ACoth function calculates the angle whose hyperbolic cotangent equals the input value.
Mathematical Properties
Function Properties
- Domain: (-∞, -1) ∪ (1, ∞) (|x| > 1)
- Range: ℝ (all real numbers)
- Discontinuity: Gap at interval [-1, 1]
- Symmetry: Odd function ACoth(-x) = -ACoth(x)
Two-Branch Properties
- Positive branch for x > 1
- Negative branch for x < -1
- Vertical asymptotes at x = ±1
- Each branch is monotonically decreasing
Applications
- Statistical Mechanics: Phase transitions
- Signal Processing: Inverse transformations
- Mathematical Physics: Soliton theory
- Engineering: Control system analysis
Practical Notes
- Domain restriction: |x| > 1 (undefined for |x| ≤ 1)
- Two separate branches with gap at [-1, 1]
- Odd function: ACoth(-x) = -ACoth(x)
- Inverse relation: Coth(ACoth(x)) = x for |x| > 1
Calculation Examples
Positive Branch
ACoth(2) ≈ 0.549
ACoth(3) ≈ 0.347
ACoth(5) ≈ 0.203
Negative Branch
ACoth(-2) ≈ -0.549
ACoth(-3) ≈ -0.347
ACoth(-5) ≈ -0.203
Invalid Inputs
ACoth(0) = NaN
ACoth(0.5) = NaN
-1 ≤ x ≤ 1: undefined
Mathematical and Physical Applications
Statistical Mechanics
Phase Transitions:
Critical behavior analysis
Two-state system models
Application: Ising model and magnetic phase transitions.
Signal Processing
Inverse Transforms:
Nonlinear signal recovery
Two-branch inverse mapping
Example: Inverse hyperbolic transformations in communications.
Important Mathematical Relationships
Inverse Function Properties
Identities: Fundamental inverse relationships.
Calculus Properties
Derivative: Rational function form.
|
|
|
|