Hyperbolic Cotangent
Online calculator for calculating the hyperbolic cotangent of an angle
Coth Calculator
Zero Exclusion
The Coth(x) or hyperbolic cotangent shows reciprocal behavior with singularity at x = 0.
Coth Function Curve
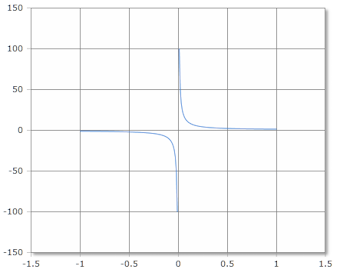
The Coth function has a vertical asymptote at x = 0 and horizontal asymptotes at y = ±1.
Domain: ℝ \ {0}, Range: (-∞, -1) ∪ (1, ∞)
|
|
Reciprocal Behavior of Coth
The hyperbolic cotangent function exhibits characteristic reciprocal properties:
- Domain: ℝ \ {0} (all real numbers except 0)
- Range: (-∞, -1) ∪ (1, ∞)
- Singularity: Vertical asymptote at x = 0
- Reciprocal: Coth(x) = 1/Tanh(x)
- Symmetry: Odd function Coth(-x) = -Coth(x)
- Asymptotes: Horizontal at y = ±1
Exponential Representation of Coth Function
The hyperbolic cotangent function is expressed through exponential functions:
Basic Formula
Ratio of hyperbolic functions for x ≠ 0
Reciprocal Relation
Reciprocal of hyperbolic tangent
Formulas for the Coth Function
Definition
Ratio of hyperbolic cosine to hyperbolic sine
Alternative Forms
Various equivalent expressions
Derivative
Derivative involves hyperbolic cosecant
Symmetry Property
Odd function (antisymmetric)
Asymptotic Behavior
Vertical asymptote at origin, horizontal at ±1
Special Values
Important Values
Singularity
Function has vertical asymptote at x = 0
Range Restriction
Values never between -1 and 1
Properties
- Reciprocal function
- Odd function symmetry
- Vertical asymptote at x = 0
- Horizontal asymptotes at y = ±1
Reciprocal Relation
Perfect reciprocal of hyperbolic tangent
Applications
Statistical mechanics, plasma physics, signal processing, mathematical analysis.
Detailed Description of the Coth Function
Definition and Input
The hyperbolic cotangent function Coth(x) is the ratio of hyperbolic cosine to hyperbolic sine. It exhibits characteristic reciprocal behavior as the reciprocal of the hyperbolic tangent function.
Input
The angle is given in degrees (full circle = 360°) or radians (full circle = 2π). The unit of measurement used is set using the Degrees or Radians menu. Note: The function is undefined at x = 0.
Result
The result is always greater than 1 for positive arguments or less than -1 for negative arguments. The function never takes values between -1 and 1.
Using the Calculator
Enter any angle value except 0. The Coth function calculates the hyperbolic cotangent, which is the reciprocal of the hyperbolic tangent.
Mathematical Properties
Function Properties
- Domain: ℝ \ {0} (all real numbers except 0)
- Range: (-∞, -1) ∪ (1, ∞)
- Singularity: Vertical asymptote at x = 0
- Symmetry: Odd function Coth(-x) = -Coth(x)
Reciprocal Properties
- Reciprocal of hyperbolic tangent function
- Vertical asymptote at x = 0
- Horizontal asymptotes at y = ±1
- Two separate branches on either side of x = 0
Applications
- Statistical Mechanics: Partition functions
- Plasma Physics: Debye-Hückel theory
- Signal Processing: Filter design
- Mathematical Analysis: Special functions
Practical Notes
- Singularity at x = 0: Function diverges to ±∞
- Range restriction: |Coth(x)| > 1 for all x ≠ 0
- Odd function: Coth(-x) = -Coth(x)
- Reciprocal relation: Coth(x) = 1/Tanh(x)
Calculation Examples
Small Positive Values
Coth(0.5) ≈ 2.164
Coth(1) ≈ 1.313
Coth(2) ≈ 1.037
Negative Values
Coth(-0.5) ≈ -2.164
Coth(-1) ≈ -1.313
Coth(-2) ≈ -1.037
Asymptotic Behavior
x → 0⁺: Coth(x) → +∞
x → 0⁻: Coth(x) → -∞
x → ±∞: Coth(x) → ±1
Physics and Engineering Applications
Statistical Mechanics
Partition Functions:
Z = 2·sinh(βħω/2) → Coth(βħω/2)
Quantum harmonic oscillator
Application: Thermal properties of quantum systems.
Plasma Physics
Debye-Hückel Theory:
Screening in ionic solutions
Electrostatic potential calculations
Example: Ion interaction in plasma environments.
Important Mathematical Relationships
Reciprocal Function Properties
Reciprocal Relationship: Perfect inverse of hyperbolic tangent.
Calculus Properties
Derivative: Negative cosecant squared.
|
|
|
|