Inverse Hyperbolic Cosecant
Online calculator for calculating the angle to the inverse hyperbolic cosecant
ACsch Calculator
Zero Exclusion
The ACsch(x) or inverse hyperbolic cosecant shows inverse function behavior with domain x ≠ 0.
Complex Numbers
You can find the ACsch function for calculating a complex number here
ACsch Function Curve
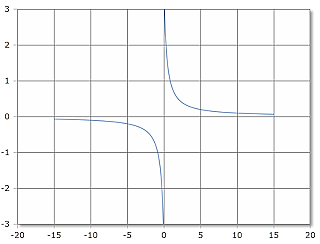
The ACsch function has two separate branches with a pole at x = 0.
Domain: ℝ \ {0}, Range: ℝ
|
|
Inverse Function Behavior of ACsch
The inverse hyperbolic cosecant function exhibits characteristic inverse properties:
- Domain: ℝ \ {0} (all real numbers except 0)
- Range: ℝ (all real numbers)
- Singularity: Pole at x = 0
- Inverse: Csch(ACsch(x)) = x for x ≠ 0
- Symmetry: Odd function ACsch(-x) = -ACsch(x)
- Branches: Two continuous branches
Logarithmic Representation of ACsch Function
The inverse hyperbolic cosecant function is expressed through logarithmic functions:
Basic Formula
Natural logarithm expression for x ≠ 0
Inverse Relation
For x ≠ 0
Formulas for the ACsch Function
Definition
Natural logarithm expression for x ≠ 0
Alternative Form
Alternative logarithmic representation
Derivative
First derivative for x ≠ 0
Symmetry Property
Odd function (antisymmetric)
Limit Behavior
Pole at origin and asymptotic behavior
Special Values
Important Values
Singularity
Function has a pole at x = 0
Asymptotic Behavior
Approaches zero as x approaches ±∞
Properties
- Inverse function
- Odd function symmetry
- Pole at origin
- Two continuous branches
Zero Behavior
Horizontal asymptote at y = 0
Applications
Signal processing, inverse problems, mathematical physics, numerical analysis.
Detailed Description of the ACsch Function
Definition and Input
The inverse hyperbolic cosecant function ACsch(x) is the inverse function of the hyperbolic cosecant. It exhibits characteristic pole behavior with a singularity at the origin.
Input
The argument can be a positive or negative number. If 0 is entered, the result is ∞ (infinity).
Result
The result is given in degrees (full circle = 360°) or radians (full circle = 2π). The unit of measurement used is set using the Degrees or Radians menu.
Using the Calculator
Enter any non-zero value. The ACsch function calculates the angle whose hyperbolic cosecant equals the input value.
Mathematical Properties
Function Properties
- Domain: ℝ \ {0} (all real numbers except 0)
- Range: ℝ (all real numbers)
- Singularity: Pole at x = 0
- Symmetry: Odd function ACsch(-x) = -ACsch(x)
Pole Properties
- Vertical asymptote at x = 0
- Approaches +∞ as x → 0⁺
- Approaches -∞ as x → 0⁻
- Two continuous branches separated by pole
Applications
- Signal Processing: Inverse transformations
- Mathematical Physics: Singular solutions
- Numerical Analysis: Pole handling
- Engineering: Reciprocal system analysis
Practical Notes
- Pole at x = 0: Function diverges to ±∞
- Odd function: ACsch(-x) = -ACsch(x)
- Inverse relation: Csch(ACsch(x)) = x for x ≠ 0
- Asymptotic approach to zero for large |x|
Calculation Examples
Small Values
ACsch(0.1) ≈ 2.993
ACsch(0.5) ≈ 1.444
ACsch(1) ≈ 0.881
Negative Values
ACsch(-0.1) ≈ -2.993
ACsch(-1) ≈ -0.881
ACsch(-2) ≈ -0.481
Limit Behavior
x → 0⁺: ACsch(x) → +∞
x → 0⁻: ACsch(x) → -∞
x → ±∞: ACsch(x) → 0
Mathematical and Physical Applications
Signal Processing
Inverse Transforms:
Reciprocal signal recovery
Pole-based filtering
Application: Inverse cosecant transforms in communications.
Numerical Analysis
Pole Handling:
Singular point analysis
Reciprocal function inverses
Example: Handling singularities in computational methods.
Important Mathematical Relationships
Inverse Function Properties
Identities: Fundamental inverse relationships.
Calculus Properties
Derivative: Involves absolute value and square root.
|
|
|
|