ASin - Arcsine (Inverse Sine)
Online calculator for calculating the angle to a sine
Arcsine Calculator
Instructions
Enter the value of the sine (between -1 and +1), select the unit of measure (degrees or radians) and click Calculate.
Arcsine - Overview
Value Range
The value of the argument must be between -1 and +1.
- Domain: x ∈ [-1, 1]
- Range: [-π/2, π/2] in radians or [-90°, 90°]
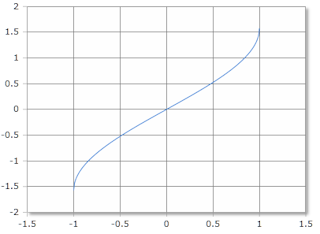
Inverse sine, scale in radians
Definition
The arcsine (Arcsin or Asin) is the inverse function of the sine function. It calculates the angle for a given sine value.
\(\displaystyle y = \arcsin(x) \Leftrightarrow \sin(y) = x \)
with \( x \in [-1, 1] \) and \( y \in [-\frac{\pi}{2}, \frac{\pi}{2}] \) (radians)
Conversion
From radians to degrees:
\(\displaystyle \text{Degrees} = \frac{\text{Radians} \cdot 180°}{\pi} \)
|
|
Description of the Arcsine
Fundamentals
The arcsine (\( \arcsin \) or \( \text{asin} \)) is the inverse function of the sine function. While the sine assigns a value between -1 and 1 to an angle, the arcsine assigns values between -1 and 1 to their corresponding angles again.
Mathematical Definition:
\(\displaystyle y = \arcsin(x) \)
means
\(\displaystyle \sin(y) = x \)
Calculating the Sine Value
The sine is a trigonometric function related to a right triangle. In a right triangle, the sine of an angle α is the ratio of the length of the opposite side to the hypotenuse:
\(\displaystyle \sin(\alpha) = \frac{\text{Opposite side}}{\text{Hypotenuse}} \)
Important: The sine value is always between -1 and 1, and an angle of 0 degrees has a sine value of 0.
Detailed Examples
Example 1: Calculate Sine Value
Given:
A right triangle with:
- Opposite side: a = 3
- Hypotenuse: c = 6
Calculating the sine:
\(\displaystyle \sin(\alpha) = \frac{3}{6} = 0.5 \)
Example 2: Calculate Angle
Task:
Calculate the angle α for \( \sin(\alpha) = 0.5 \)
In radians:
\(\displaystyle \alpha = \arcsin(0.5) = \frac{\pi}{6} \approx 0.524 \text{ rad} \)
Conversion to degrees:
\(\displaystyle \alpha = 30° \)
Verification: sin(30°) = 0.5 ✓
Example 3: Common Values
Important sine values:
- \( \arcsin(0) = 0° = 0 \text{ rad} \)
- \( \arcsin(0.5) = 30° = \frac{\pi}{6} \text{ rad} \)
- \( \arcsin(\frac{\sqrt{2}}{2}) = 45° = \frac{\pi}{4} \text{ rad} \)
- \( \arcsin(\frac{\sqrt{3}}{2}) = 60° = \frac{\pi}{3} \text{ rad} \)
- \( \arcsin(1) = 90° = \frac{\pi}{2} \text{ rad} \)
Conversion Formula
From radians to degrees:
\(\displaystyle \text{Degrees} = \frac{\text{Radians} \cdot 180°}{\pi} \)
Properties
- Domain: \( x \in [-1, 1] \)
- Range: \( y \in [-\frac{\pi}{2}, \frac{\pi}{2}] \) (radians) or \( [-90°, 90°] \)
- Monotonicity: Strictly monotonically increasing
- Symmetry: Odd function: \( \arcsin(-x) = -\arcsin(x) \)
- Special values:
- \( \arcsin(0) = 0 \)
- \( \arcsin(1) = \frac{\pi}{2} \approx 90° \)
- \( \arcsin(-1) = -\frac{\pi}{2} \approx -90° \)
Practical Applications
- Geometry: Angle calculation in triangles
- Navigation: Course determination and positioning
- Physics: Projectile motion and wave analysis
- Computer graphics: 3D rotations and projections
- Robotics: Joint angle calculations
- Astronomy: Calculation of celestial coordinates
- Engineering: Structural analysis and design
Relationship to Other Functions
Relationship to arccosine:
\(\displaystyle \arcsin(x) + \arccos(x) = \frac{\pi}{2} \)
Derivative:
\(\displaystyle \frac{d}{dx}\arcsin(x) = \frac{1}{\sqrt{1-x^2}} \)
Important Note
Notation: In programming and mathematical software, the arcsine function is typically called asin or arcsin. The notation sin⁻¹(x) can be confusing as it might be mistaken for the reciprocal function (1/sin(x)), which is actually the cosecant (csc(x)).
Multiple solutions: Since the sine function is periodic, there are infinitely many angles with the same sine value. The arcsine function returns the principal value in the range [-90°, 90°] or [-π/2, π/2].
|
|