Csc - Calculate Cosecant
Online calculator for calculating the cosecant of an angle
Cosecant Calculator
Instructions
Enter the angle whose cosecant you want to calculate, select the unit of measure (degrees or radians) and click Calculate.
Cosecant - Overview
Value Range
The angle is given in degrees (full circle = 360°) or radians (full circle = 2·π).
Note: The cosecant is undefined at 0°, 180°, 360° (or 0, π, 2π in radians) where sin(α) = 0.
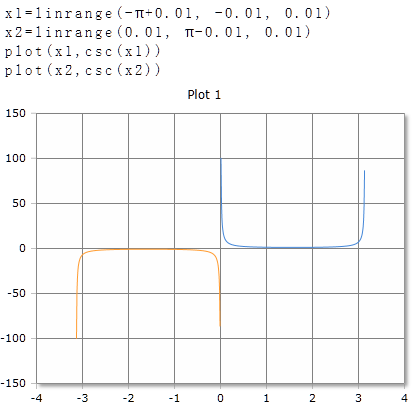
Cosecant, scale in radians
Definition in Triangle
The cosecant is the reciprocal of the sine function. In a right triangle, it is the ratio of the hypotenuse to the opposite side.
\(\displaystyle \csc(\alpha) = \frac{\text{Hypotenuse}}{\text{Opposite}} = \frac{c}{a} = \frac{1}{\sin(\alpha)} \)

Important Values
- \( \csc(30°) = 2 \)
- \( \csc(45°) = \sqrt{2} \approx 1.414 \)
- \( \csc(60°) = \frac{2}{\sqrt{3}} \approx 1.155 \)
- \( \csc(90°) = 1 \)
- \( \csc(0°) = \) undefined (∞)
- \( \csc(180°) = \) undefined (∞)
|
|
Description of the Cosecant
Fundamentals
The cosecant (csc) is one of the six basic trigonometric functions. It is the reciprocal of the sine function. In a right triangle, the cosecant of an angle α is the ratio of the hypotenuse to the opposite side.
Definition:
\(\displaystyle \csc(\alpha) = \frac{\text{Hypotenuse}}{\text{Opposite}} = \frac{c}{a} \)
\(\displaystyle \csc(\alpha) = \frac{1}{\sin(\alpha)} \)
Properties
The cosecant function has several important properties:
- Periodic: csc(α + 360°) = csc(α)
- Odd function: csc(-α) = -csc(α)
- Undefined: At 0°, ±180°, ±360°, ... (where sin(α) = 0)
- Range: (-∞, -1] ∪ [1, +∞)
- Domain: All real numbers except multiples of 180° (or π)
Relationship to Other Functions
The cosecant is related to other trigonometric functions:
\(\displaystyle \csc(\alpha) = \frac{1}{\sin(\alpha)} \)
\(\displaystyle \sin(\alpha) = \frac{1}{\csc(\alpha)} \)
\(\displaystyle 1 + \cot^2(\alpha) = \csc^2(\alpha) \)
Detailed Examples
Example 1: Calculate Cosecant
Given:
A right triangle with:
- Hypotenuse: \( c = 10 \text{ cm} \)
- Opposite side: \( a = 6 \text{ cm} \)
Calculation:
\(\displaystyle \csc(\alpha) = \frac{10}{6} \approx 1.667 \)
To find the angle: \( \alpha = \arcsin\left(\frac{6}{10}\right) \approx 36.87° \)
Example 2: Known Angles
Important cosecant values:
| \( \csc(30°) \) | = | 2 |
| \( \csc(45°) \) | = | \( \sqrt{2} \approx 1.414 \) |
| \( \csc(60°) \) | = | \( \frac{2}{\sqrt{3}} \approx 1.155 \) |
| \( \csc(90°) \) | = | 1 |
| \( \csc(120°) \) | = | \( \frac{2}{\sqrt{3}} \approx 1.155 \) |
| \( \csc(150°) \) | = | 2 |
Example 3: Using Sine
Task:
If \( \sin(\alpha) = 0.5 \), what is \( \csc(\alpha) \)?
Solution:
\(\displaystyle \csc(\alpha) = \frac{1}{\sin(\alpha)} = \frac{1}{0.5} = 2 \)
This corresponds to α = 30° (or π/6 rad)
Conversion
From degrees to radians:
\(\displaystyle \text{Radians} = \frac{\text{Degrees} \cdot \pi}{180°} \)
Mathematical Properties
- Period: 360° or 2π (radians)
- Symmetry: Odd function: csc(-α) = -csc(α)
- Asymptotes: Vertical at 0°, ±180°, ±360°, ...
- Minimum value: |csc(α)| ≥ 1
- Reciprocal: csc(α) = 1/sin(α)
- Pythagorean identity: 1 + cot²(α) = csc²(α)
- Relationship to arcsine:
- \( \text{arccsc}(x) = \arcsin\left(\frac{1}{x}\right) \)
Practical Applications
- Physics: Wave mechanics and oscillations
- Engineering: Structural analysis
- Optics: Light refraction calculations
- Navigation: Distance and bearing calculations
- Astronomy: Celestial coordinate systems
- Signal processing: Amplitude analysis
- Mathematics: Solving trigonometric equations
- Computer graphics: 3D rendering and projections
Important Note
The cosecant function is undefined at angles where the sine equals zero (0°, ±180°, ±360°, ... or 0, ±π, ±2π, ...). At these points, the function approaches positive or negative infinity. The cosecant is the reciprocal of the sine: csc(α) = 1/sin(α). Since |sin(α)| ≤ 1, the absolute value of the cosecant is always ≥ 1: |csc(α)| ≥ 1. The function has a period of 360° (or 2π radians), meaning csc(α + 360°) = csc(α). The cosecant function is particularly useful in solving trigonometric equations and in applications involving wave mechanics and oscillations.
|
|