ACot - Arccotangent (Inverse Cotangent)
Online calculator for calculating the angle to the cotangent
Arccotangent Calculator
Instructions
Enter the value of the cotangent, select the unit of measure (degrees or radians) and click Calculate.
Arccotangent - Overview
Value Range
The arccotangent accepts all real numbers as input.
- Domain: All real numbers (-∞, +∞)
- Range: (0, π) in radians or (0°, 180°)
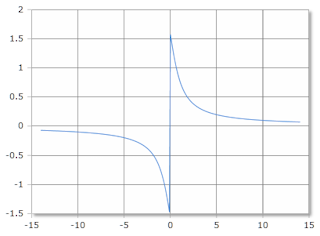
Inverse cotangent, scale in radians
Definition
The arccotangent (arccot, acot, or cot⁻¹) is the inverse function of the cotangent function.
\(\displaystyle y = \text{arccot}(x) \Leftrightarrow \cot(y) = x \)
with \( x \in \mathbb{R} \) and \( y \in (0, \pi) \)
Relationship
Relationship to arctangent:
\(\displaystyle \text{arccot}(x) = \frac{\pi}{2} - \arctan(x) \)
|
|
Description of the Arccotangent
Fundamentals
The arccotangent (arccot, acot, or cot⁻¹) is the inverse function of the cotangent function. It calculates the angle for a given cotangent value. The function is used in mathematics, engineering, physics, and geometry to find angles based on trigonometric ratios.
Mathematical Definition:
\(\displaystyle y = \text{arccot}(x) \)
means
\(\displaystyle \cot(y) = x \)
Understanding Cotangent
In a right triangle, the cotangent of an angle α is the ratio of the adjacent side to the opposite side:
\(\displaystyle \cot(\alpha) = \frac{\text{Adjacent}}{\text{Opposite}} = \frac{b}{a} \)
Also: \(\displaystyle \cot(\alpha) = \frac{1}{\tan(\alpha)} = \frac{\cos(\alpha)}{\sin(\alpha)} \)
Important: The cotangent is the reciprocal of the tangent function.
Detailed Examples
Example 1: Calculate Cotangent Value
Given:
A right triangle with:
- Adjacent side: \( b = 4 \)
- Opposite side: \( a = 3 \)
Calculating the cotangent:
\(\displaystyle \cot(\alpha) = \frac{4}{3} \approx 1.333 \)
Example 2: Calculate Angle
Task:
Calculate the angle α for \( \cot(\alpha) = 1.333 \)
In radians:
\(\displaystyle \alpha = \text{arccot}(1.333) \approx 0.6435 \text{ rad} \)
Conversion to degrees:
\(\displaystyle \alpha = \frac{0.6435 \cdot 180°}{\pi} \approx 36.87° \)
Example 3: Special Values
Common cotangent values:
- \( \text{arccot}(1) = 45° = \frac{\pi}{4} \text{ rad} \)
- \( \text{arccot}(0) = 90° = \frac{\pi}{2} \text{ rad} \)
- \( \text{arccot}(\sqrt{3}) = 30° = \frac{\pi}{6} \text{ rad} \)
Conversion Formula
From radians to degrees:
\(\displaystyle \text{Degrees} = \frac{\text{Radians} \cdot 180°}{\pi} \)
Properties
- Domain: \( x \in \mathbb{R} \) (all real numbers)
- Range: \( y \in (0, \pi) \) (radians) or \( (0°, 180°) \)
- Monotonicity: Strictly monotonically decreasing
- Asymptotes: Horizontal asymptotes at y = 0 and y = π
- Special values:
- \( \text{arccot}(\infty) = 0 \)
- \( \text{arccot}(1) = \frac{\pi}{4} \approx 45° \)
- \( \text{arccot}(0) = \frac{\pi}{2} \approx 90° \)
- \( \text{arccot}(-\infty) = \pi \approx 180° \)
Practical Applications
- Geometry: Angle calculations in triangles
- Engineering: Structural analysis and design
- Physics: Wave analysis and optics
- Navigation: Direction and bearing calculations
- Computer graphics: 3D transformations
- Signal processing: Phase angle calculations
- Surveying: Land measurement and mapping
Relationships to Other Functions
Tangent relationship:
\(\displaystyle \tan(\alpha) = \frac{1}{\cot(\alpha)} \)
\(\displaystyle \cot(\alpha) = \frac{1}{\tan(\alpha)} \)
Arctangent relationship:
\(\displaystyle \text{arccot}(x) = \frac{\pi}{2} - \arctan(x) \)
\(\displaystyle \text{arccot}(x) = \arctan\left(\frac{1}{x}\right) \text{ for } x > 0 \)
Cotangent in Terms of Sine and Cosine
\(\displaystyle \cot(\alpha) = \frac{\cos(\alpha)}{\sin(\alpha)} \)
This shows the cotangent as the ratio of cosine to sine
Important Note
Notation: The notation cot⁻¹(x) can be confusing as it might be mistaken for the reciprocal function (1/cot(x)). In programming and mathematical software, the functions are typically called acot or arccot to avoid this confusion.
Programming: Not all programming languages have a built-in
arccotangent function. It can be calculated using: acot(x) = atan(1/x)
for positive x, with appropriate adjustments for negative values.
|
|