Inverse Hyperbolic Sine
Online calculator for calculating the angle to the inverse hyperbolic sine
ASinh Calculator
Unrestricted Domain
The ASinh(x) or inverse hyperbolic sine shows inverse function behavior for all real numbers.
ASinh Function Curve
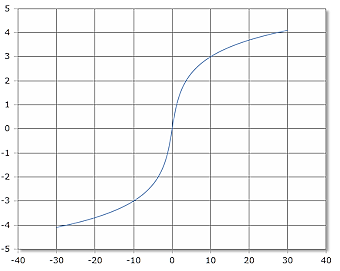
The ASinh function is defined for all real numbers and is strictly increasing.
Domain: ℝ, Range: ℝ
|
|
Inverse Function Behavior of ASinh
The inverse hyperbolic sine function exhibits characteristic inverse properties:
- Domain: ℝ (all real numbers)
- Range: ℝ (all real numbers)
- Zero Point: ASinh(0) = 0
- Inverse: Sinh(ASinh(x)) = x for all x
- Symmetry: Odd function ASinh(-x) = -ASinh(x)
- Monotonicity: Strictly increasing
Logarithmic Representation of ASinh Function
The inverse hyperbolic sine function is expressed through logarithmic functions:
Basic Formula
Natural logarithm expression for all x ∈ ℝ
Inverse Relation
For all x ∈ ℝ
Formulas for the ASinh Function
Definition
Natural logarithm expression for all x ∈ ℝ
Inverse Relation
Perfect inverse function properties
Derivative
First derivative for all x ∈ ℝ
Symmetry Property
Odd function (antisymmetric)
Asymptotic Behavior
Logarithmic growth for large arguments
Special Values
Important Values
Unrestricted Domain
Function defined everywhere
Zero Point
Function passes through origin
Properties
- Inverse function
- Strictly increasing
- Odd function symmetry
- Unrestricted domain
Growth Pattern
Logarithmic growth pattern
Applications
Relativistic physics, engineering calculations, signal processing, mathematical modeling.
Detailed Description of the ASinh Function
Definition and Input
The inverse hyperbolic sine function ASinh(x) is the inverse function of the hyperbolic sine. It exhibits characteristic unrestricted domain behavior, making it the most versatile inverse hyperbolic function.
Input
The argument can be a positive or negative number. There are no domain restrictions - all real numbers are valid inputs.
Result
The result is given in degrees (full circle = 360°) or radians (full circle = 2π). The unit of measurement used is set using the Degrees or Radians menu.
Using the Calculator
Enter any real number. The ASinh function calculates the angle whose hyperbolic sine equals the input value.
Mathematical Properties
Function Properties
- Domain: ℝ (all real numbers)
- Range: ℝ (all real numbers)
- Zero Point: ASinh(0) = 0
- Symmetry: Odd function ASinh(-x) = -ASinh(x)
Unrestricted Properties
- No domain restrictions or singularities
- Continuous and differentiable everywhere
- Perfect inverse of Sinh function
- Logarithmic growth for large arguments
Applications
- Relativistic Physics: Velocity calculations
- Engineering: Cable and chain problems
- Signal Processing: Amplitude transformations
- Mathematical Modeling: Growth processes
Practical Notes
- No domain restrictions: accepts any real number
- Origin passage: ASinh(0) = 0
- Odd function: ASinh(-x) = -ASinh(x)
- Perfect inverse: Sinh(ASinh(x)) = x for all x
Calculation Examples
Small Values
ASinh(0) = 0
ASinh(0.5) ≈ 0.481
ASinh(1) ≈ 0.881
Negative Values
ASinh(-0.5) ≈ -0.481
ASinh(-1) ≈ -0.881
ASinh(-2) ≈ -1.444
Large Values
ASinh(10) ≈ 2.993
ASinh(100) ≈ 5.298
Logarithmic growth
Mathematical and Physical Applications
Relativistic Physics
Velocity Addition:
v = c · tanh(ASinh(v₁/c) + ASinh(v₂/c))
Relativistic velocity composition
Application: Calculating combined relativistic velocities.
Engineering Applications
Catenary Problems:
Cable tension analysis
Chain and rope calculations
Example: Suspension bridge cable shape analysis.
Important Mathematical Relationships
Perfect Inverse Properties
Perfect Inverse: No domain restrictions on either side.
Calculus Properties
Derivative: Always positive, ensuring strict monotonicity.
|
|
|
|