Hyperbolic Cosine
Online calculator for calculating the hyperbolic cosine of an angle
Cosh Calculator
Universal Domain
The Cosh(x) or hyperbolic cosine shows catenary curve behavior for all real numbers.
Cosh Function Curve
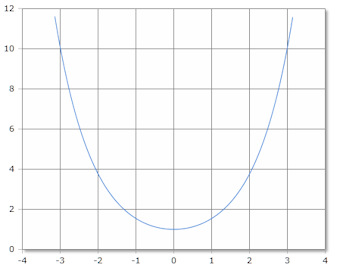
The Cosh function forms a catenary curve with minimum value 1 at x = 0.
Domain: ℝ, Range: [1, ∞)
|
|
Catenary Curve Behavior of Cosh
The hyperbolic cosine function exhibits characteristic catenary properties:
- Domain: ℝ (all real numbers)
- Range: [1, ∞) (values ≥ 1)
- Minimum: Cosh(0) = 1
- Symmetry: Even function Cosh(-x) = Cosh(x)
- Growth: Exponential for large |x|
- Shape: Classic catenary curve
Exponential Representation of Cosh Function
The hyperbolic cosine function is expressed through exponential functions:
Basic Formula
Average of exponential and its reciprocal
Catenary Relation
Hanging chain equation
Formulas for the Cosh Function
Definition
Exponential average for all x ∈ ℝ
Catenary Equation
Shape of hanging cables and chains
Derivative
Derivative is hyperbolic sine
Symmetry Property
Even function (symmetric about y-axis)
Hyperbolic Identity
Fundamental hyperbolic identity
Special Values
Important Values
Universal Domain
Function defined everywhere
Minimum Value
Minimum value is 1 at x = 0
Properties
- Even function
- Always positive
- Catenary curve shape
- Exponential growth
Growth Pattern
Exponential growth for large arguments
Applications
Engineering (cables, chains), architecture, physics, mathematical modeling.
Detailed Description of the Cosh Function
Definition and Input
The hyperbolic cosine function Cosh(x) is defined as the average of exponential functions. It exhibits characteristic catenary curve behavior representing the shape of hanging cables and chains.
Input
The angle is given in degrees (full circle = 360°) or radians (full circle = 2π). The unit of measurement used is set using the Degrees or Radians menu.
Result
The result is always greater than or equal to 1, with the minimum value occurring at x = 0. The function grows exponentially for large positive or negative arguments.
Using the Calculator
Enter any angle value. The Cosh function calculates the hyperbolic cosine, which represents the catenary curve equation.
Mathematical Properties
Function Properties
- Domain: ℝ (all real numbers)
- Range: [1, ∞) (values ≥ 1)
- Minimum: Cosh(0) = 1
- Symmetry: Even function Cosh(-x) = Cosh(x)
Catenary Properties
- Represents shape of hanging cables and chains
- Minimum energy configuration under gravity
- U-shaped curve with vertex at (0, 1)
- Exponential growth for large arguments
Applications
- Engineering: Cable and chain calculations
- Architecture: Arch and bridge design
- Physics: Wave equations and relativity
- Mathematics: Special relativity and geometry
Practical Notes
- No domain restrictions: accepts any real number
- Always positive: Cosh(x) ≥ 1 for all x
- Even function: Cosh(-x) = Cosh(x)
- Catenary shape: Natural curve of hanging objects
Calculation Examples
Basic Values
Cosh(0) = 1
Cosh(1) ≈ 1.543
Cosh(2) ≈ 3.762
Special Values
Cosh(ln(2)) = 1.25
Cosh(ln(3)) ≈ 1.667
Cosh(π) ≈ 11.592
Large Arguments
Cosh(5) ≈ 74.21
Cosh(10) ≈ 11013.2
Exponential growth
Engineering and Physical Applications
Catenary Engineering
Cable Shape:
y = a·Cosh(x/a)
Natural shape of hanging cables
Application: Bridge design, power lines, suspension structures.
Wave Physics
Wave Solutions:
ψ(x,t) = A·Cosh(kx)·e^(-iωt)
Evanescent wave solutions
Example: Quantum tunneling, electromagnetic waves.
Important Mathematical Relationships
Hyperbolic Identity
Fundamental Identity: Analogous to trigonometric identity.
Calculus Properties
Derivative: Derivative is hyperbolic sine.
|
|
|
|