Hyperbolic Tangent
Calculator and formula for calculating the hyperbolic tangent of an angle
Tanh Calculator
Sigmoid Function
The Tanh(x) or hyperbolic tangent shows sigmoid behavior with range [-1, 1].
Complex Numbers
You can find the Tanh function for calculating a complex number here
Tanh Function Curve
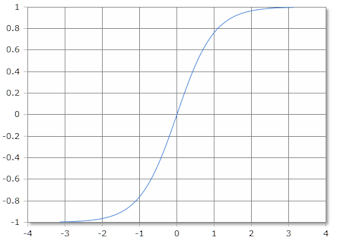
The Tanh function is S-shaped with horizontal asymptotes at y = ±1.
Domain: ℝ, Range: (-1, 1)
Unit of measurement for the X axis is radians
|
|
Sigmoid Behavior of the Tanh Function
The hyperbolic tangent function exhibits characteristic sigmoid properties:
- Domain: ℝ (all real numbers)
- Range: (-1, 1) (bounded between -1 and 1)
- Zero: Tanh(0) = 0
- Symmetry: Odd function Tanh(-x) = -Tanh(x)
- Asymptotes: Horizontal at y = ±1
- Monotonicity: Strictly monotonically increasing
Exponential Function Representation of the Tanh Function
The hyperbolic tangent function is expressed through exponential functions:
Basic Formula
Ratio of Sinh to Cosh for all x ∈ ℝ
Alternative Form
Simplified exponential form
Formulas for the Tanh Function
Definition as Ratio
Ratio of hyperbolic sine to hyperbolic cosine
Exponential Forms
Various exponential function representations
Derivative
First derivative for all x ∈ ℝ
Symmetry Property
Odd function (antisymmetric)
Limit Behavior
Horizontal asymptotes at y = ±1
Special Values
Important Values
Range
Bounded output between -1 and +1
Properties
- Odd function
- Strictly monotonically increasing
- Sigmoid S-curve
- Bounded range
Asymptotic Behavior
Exponential approach to ±1
Applications
Neural networks, machine learning, activation functions, signal processing.
Detailed Description of the Tanh Function
Definition and Input
The hyperbolic tangent function Tanh(x) is a mathematical function from the family of hyperbolic functions. It exhibits characteristic sigmoid behavior with a bounded range.
Input
The angle is given in degrees (full circle = 360°) or radians (full circle = 2π). The unit of measurement used is set using the Degrees or Radians menu. The argument can be any real number.
Output
The range of the result is -1 to +1. The function approaches these limit values asymptotically but never reaches them exactly for finite input values.
Using the Calculator
Enter any angle. The Tanh function is defined for all real numbers and always returns a value between -1 and 1.
Mathematical Properties
Function Properties
- Domain: ℝ (all real numbers)
- Range: (-1, 1) (bounded)
- Zero: Tanh(0) = 0
- Symmetry: Odd function Tanh(-x) = -Tanh(x)
Sigmoid Properties
- S-shaped curve through the origin
- Horizontal asymptotes at y = ±1
- Steep rise around x = 0
- Smooth transition between extreme values
Applications
- Neural Networks: Activation function
- Machine Learning: Sigmoid normalization
- Signal Processing: Nonlinear transformation
- Control Engineering: Saturation functions
Practical Notes
- Tanh(0) = 0: Symmetry center of the function
- Bounded: -1 < Tanh(x) < 1 for all x
- For large |x|: Tanh(x) ≈ ±1 · (1 - 2e^(-2|x|))
- For small |x|: Tanh(x) ≈ x (linear approximation)
Calculation Examples
Small Values
Tanh(0) = 0
Tanh(0.5) ≈ 0.462
Tanh(1) ≈ 0.762
Medium Values
Tanh(2) ≈ 0.964
Tanh(3) ≈ 0.995
Tanh(-2) ≈ -0.964
Limits
x → +∞: Tanh(x) → 1
x → -∞: Tanh(x) → -1
Never exactly ±1
Applications in Artificial Intelligence
Neural Networks
Activation Function:
y = tanh(wx + b)
Nonlinear transformation
Advantage: Symmetric around 0, steep gradient transitions.
Signal Processing
Saturation Function:
Limits output signals
Prevents overdrive
Application: Adaptive filters, control systems.
Important Mathematical Relationships
Relationship to Other Hyperbolic Functions
Identities: Fundamental hyperbolic relationships.
Integrals and Series
Antiderivative: Natural logarithm of Cosh.
|
|
|
|